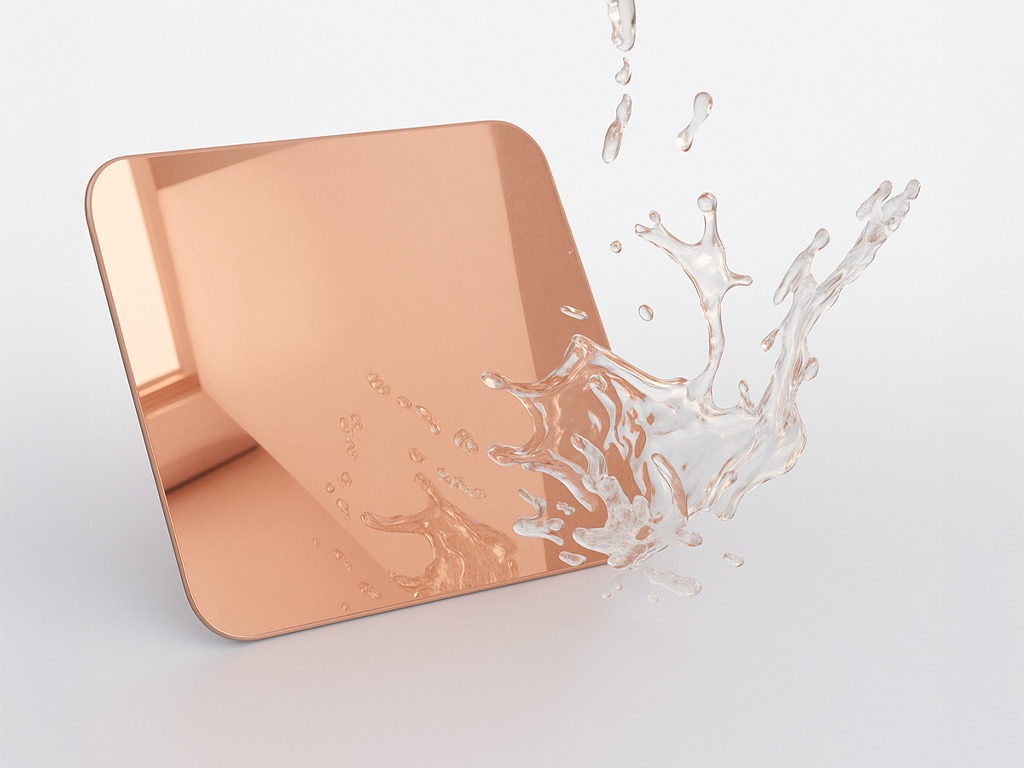
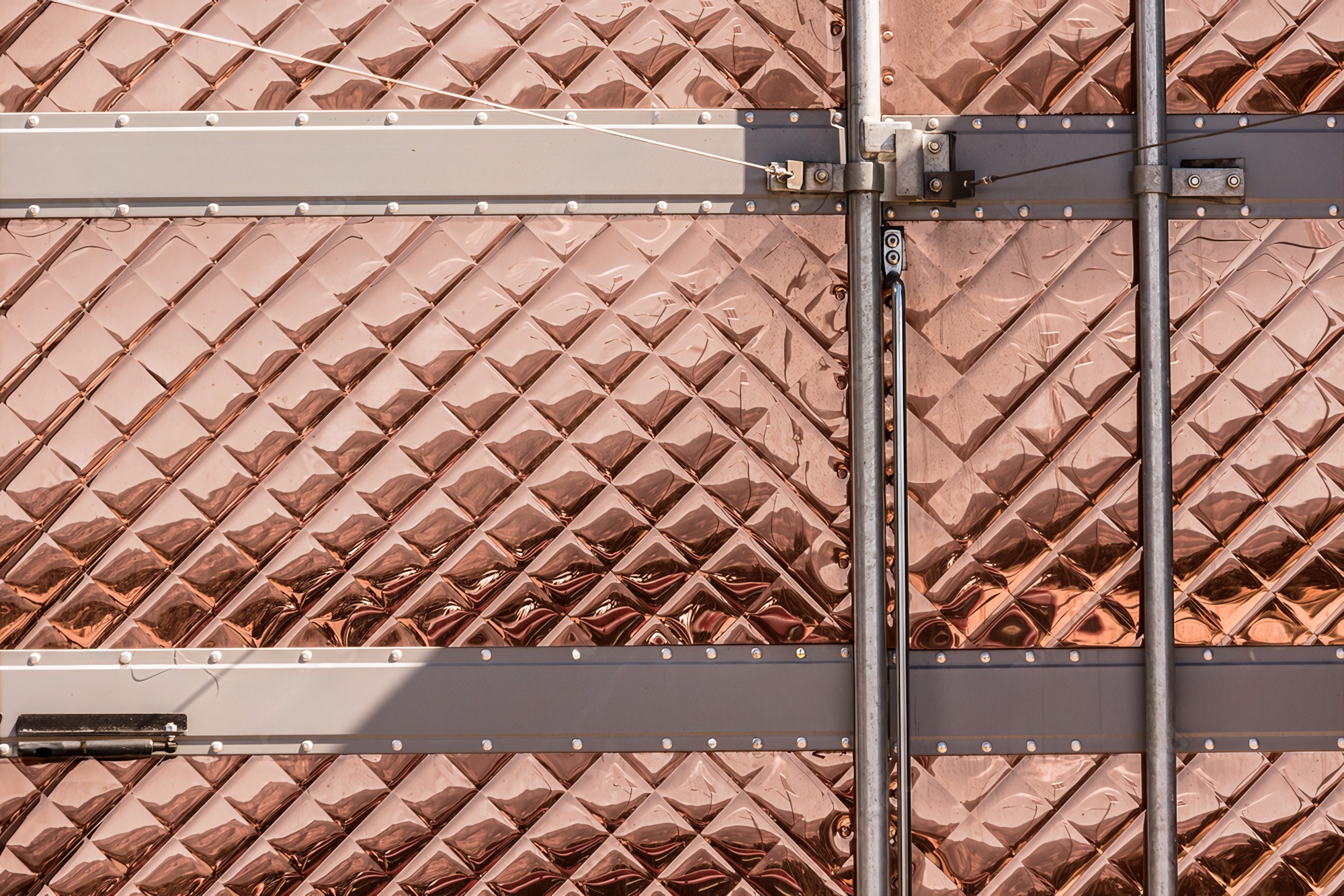
What is PVD
PVD, or Physical Vapor Deposition, is a high-performance vacuum coating process used to apply a thin, highly durable, and decorative metal layer onto stainless steel surfaces.
In a controlled high-vacuum environment, solid metal materials—such as titanium, zirconium, or chromium—are vaporized through sputtering or thermal evaporation. These vaporized particles then condense onto the stainless steel, bonding at the molecular level to the substrate. Reactive gases are added to create nitrides or oxides, producing vibrant, long-lasting colors.
The process typically follows these steps:
- Surface preparation: Stainless steel sheets are meticulously cleaned to remove any impurities that could interfere with bonding.
- Vacuum chamber: The substrate is placed in a chamber that’s evacuated to ultra-low pressures (as low as 10⁻⁶Torr).
- Metal vaporization: Metal targets are heated or bombarded with high-energy ions to create a metal vapor.
- Reactive gases: Gases like nitrogen or oxygen are introduced to form metal nitrides or oxides (e.g., TiN, ZrN), which define the coating’s color and properties.
- Deposition: The metal compound condenses into a thin, crystalline layer that is uniform, color-rich, and physically bonded to the substrate.